How Does the Diaphragm Work? Diaphragm Structure and Function
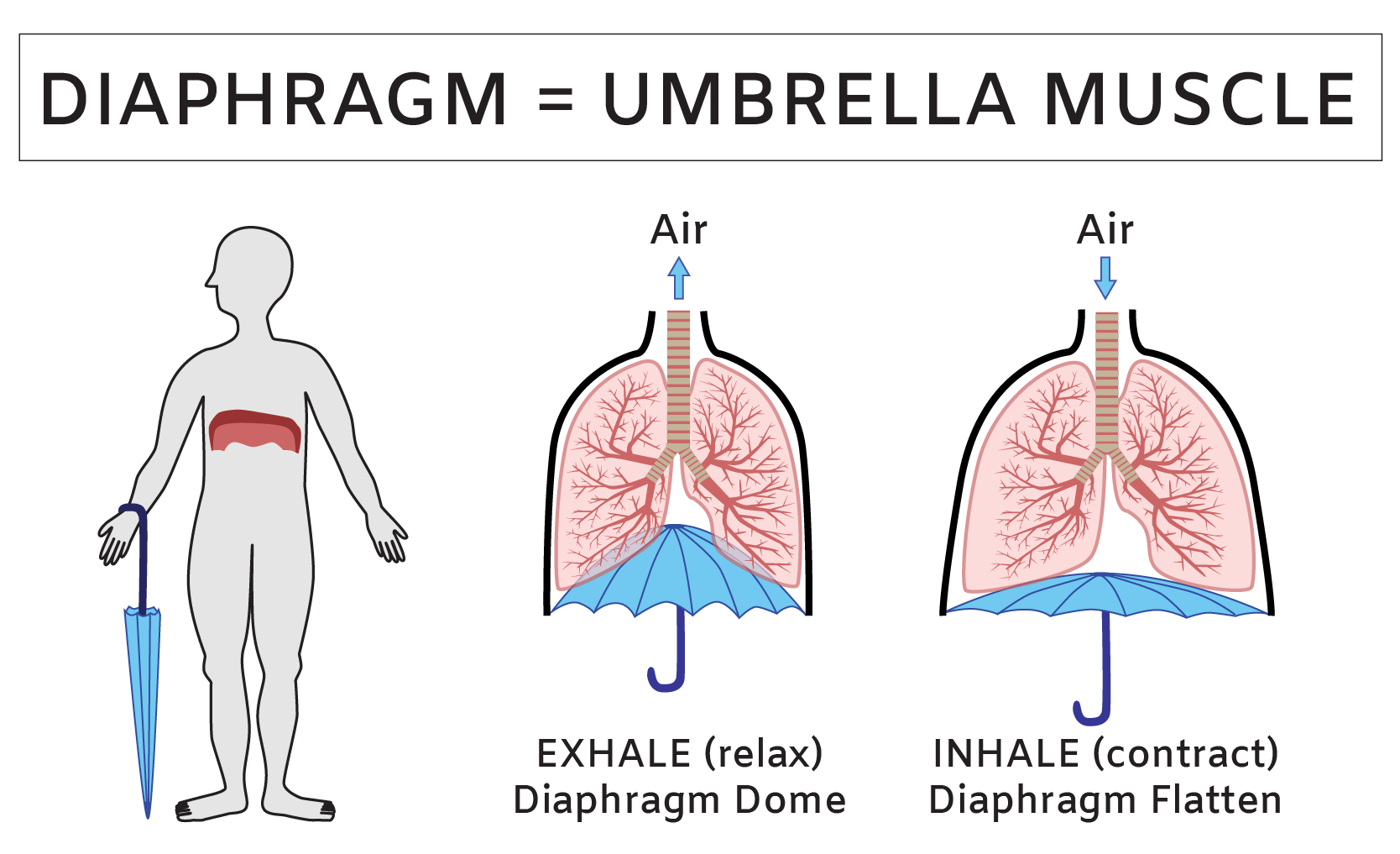
Learn More About Simplified Science PublishingThe diaphragm is a muscle that forms an umbrella dome shape at the base of your ribcage and helps you breathe.
Every breath begins with an umbrella shaped muscle that flexes underneath your ribcage. This dome-shaped muscle that stretches across your torso is called the diaphragm (die-uh-fram) and when your diaphragm is relaxed, it resembles an oblong umbrella top that is squeezed underneath your ribs and creates the base of your chest cavity.
How Does the Diaphragm Work?
The movement of the diaphragm muscle provides the primary force for every inhale and exhale that you take. When the diaphragm is relaxed, it forms a dome that presses into your chest cavity and pushes against the lungs to help push air out. When your diaphragm contracts, the dome flattens out as if it were a flexible umbrella-top that was pulled downward by the handle. As your diaphragm flattens, it creates more space and reduces pressure in the chest cavity and this pressure change forces air into your lungs. When your diaphragm muscle relaxes, it re-forms the dome shape, which reduces space in the chest cavity and allows air to flow out of the lungs.
To solidify the concept of diaphragm function, place your hand below your ribcage and pay attention to the movement underneath your hand as you take deep, belly breaths. With every inhalation, your diaphragm flattens, (pulling down on the metaphorical umbrella handle), which expands your ribcage and reduces pressure in your chest to pull air into your lungs. Now when you exhale, imagine the umbrella top pushing upward and forming the dome shape underneath your ribs. Can you feel that each exhale is guided by the diaphragm pushing back up into your chest?
Intercostal Muscles
When you breathe, you may also feel that your upper body expands. Although the diaphragm is the main force behind respiration, the muscles that fill the gaps between your ribs are also important. These thin ribcage muscles are called intercostal muscles. Let’s take a moment to meet your intercostals. Place a finger between a pair of your ribs and take a few big breaths. You should be able to feel these muscles lengthen with each inhale, (allowing your ribs to expand) and shorten with each exhale, (decreasing the volume of your chest cavity). The ability of your intercostals to expand and collapse your ribcage allows you to take bigger breaths. This function is especially important when you are active and in need of more oxygen. During exercise and other strenuous activities, the human body requires more energy and therefore more oxygen. (Remember, no oxygen = no energy).
The intercostal muscles provide structure and flexibility to your upper body and when you breathe, they allow your ribcage to expand and contract. If your entire ribcage were made of rigid bone, your lungs wouldn’t be able to expand as much. Athletes and people running away from zombies depend on both the diaphragm and the intercostal muscles to allow for deep breaths that provide hard-working cells with oxygen.
Diaphragm Injury and Disease
Diaphragm injuries are most often caused by traumatic physical events such as traffic accidents. Considering that the umbrella muscle is essential for breathing, injuries to the diaphragm results in life-threatening scenarios that require serious medical care. Doctors can use a variety of tests, such as chest X-rays, computerized tomography (CT) scans and surgical procedures, to determine whether a diaphragm is in need of surgical repair.
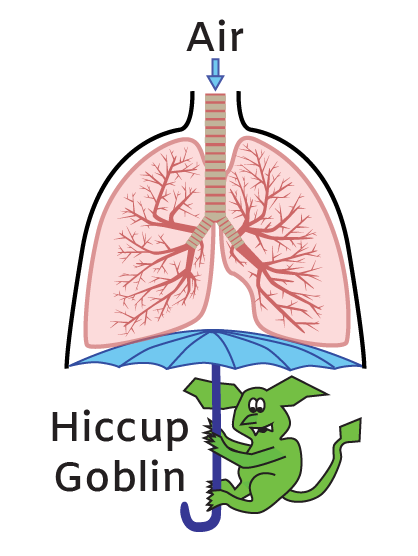
However, there is also a much more prevalent, non-vital issue that affects the diaphragm and intercostal muscles: hiccups. Those sneaky bastards come out of nowhere. The surprising moment when air is sucked into your lungs and a little “hic” sound is released from your throat can feel as though your respiratory system was hijacked. A hiccup is caused when the diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract without your control. It’s as if a little chest cavity goblin does exist and tugs down on the umbrella muscle handle.
The common hiccup is often caused by a rapid expansion of the stomach that can occur with overeating, eating too fast, eating spicy food, drinking carbonated drinks and even changes in temperature. Everyone has their favorite cure. People hold their breath, eat sugar and use surprise scare tactics with varied success. Unfortunately, a scientifically proven non-invasive hiccup treatment remains a mystery.
Diaphragm Anatomy Summary
Diaphragm: The diaphragm is the umbrella muscle that forms a dome shape at the base of your ribcage. When the diaphragm contracts, it flattens and creates more space and less pressure in the chest cavity. This reduced pressure causes air to flow into the lungs. When the diaphragm relaxes, air flows out of the lungs as the umbrella muscle re-forms the dome.
Intercostal Muscles: Muscles that fill the gaps between your ribs provide structure and flexibility to your upper body and when you breathe, they allow your ribcage to expand and contract.
Related Content:
- How Do Lungs Work? Lung Structure and Function
- What are Pleura? Lung Pleura Structure and Function
- What is the Epiglottis? Epiglottis Structure and Function
- How Does the Heart Work? Review Heart Structure and Function
- What is Blood Made Of? Review Blood Components and Functions
- What is Aerobic Respiration and Why is it Important?
References:
- Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 18th Edition. Longo DL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Jameson J, Loscalzo J. eds.
- Anatomy, Physiology, and Disease: An Interactive Journey for Health Professions , 2nd Edition. Bruce J. Colbert, University of Pittsburgh, Johnstown.
Create professional science figures with illustration services or use the online courses and templates to quickly learn how to make your own designs.
Interested in free design templates and training?
Explore scientific illustration templates and courses by creating a Simplified Science Publishing Log In. Whether you are new to data visualization design or have some experience, these resources will improve your ability to use both basic and advanced design tools.
Interested in reading more articles on scientific design? Learn more below:
Content is protected by Copyright license. Website visitors are welcome to share images and articles, however they must include the Simplified Science Publishing URL source link when shared. Thank you!